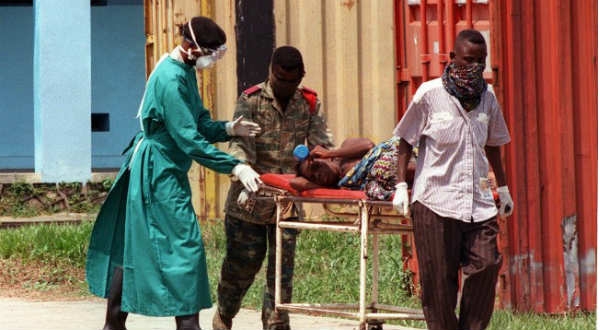
Guinea has decided to close its borders with Liberia and Sierra Leone to contain the spread of Ebola, which has killed 959 people in the three countries.
The latest Ebola outbreak is thought to have begun in Guinea, but Liberia and Sierra Leone are currently facing the highest frequency of new cases.
The World Health Organization (WHO) said on Friday the spread of the virus was a global health emergency.
The Ebola virus is transmitted between humans through bodily fluids.
Animals such as fruit bats carry the virus, which can be transmitted to humans through contact with blood or consumption of bushmeat.
In recent weeks, countries around the world have advised their citizens not to travel to the affected countries.
The infections have spread to Nigeria, which has recorded two deaths and several more cases.
The total number of cases in the current outbreak stands at 1,779, the WHO said on Friday.
The most recent figures from August 5 and 6 showed 68 new cases and 29 deaths.
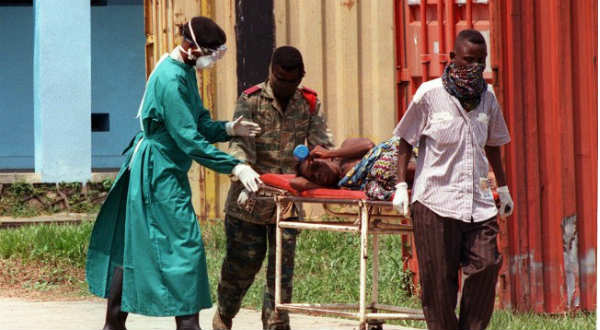
They included 26 new cases in Sierra Leone and 38 in Liberia, but no new cases in Guinea, where the outbreak began.
Guinea said it was closing its borders in order to stop people from entering the country.
“We have provisionally closed the frontier between Guinea and Sierra Leone because of all the news that we have received from there recently,” Health Minister Remy Lamah told a news conference.
Remy Lamah added that Guinea had also closed its border with Liberia.
Guinea, Sierra Leone and Liberia have already declared varying levels of emergency over the spread of the virus.
The most intense outbreak in Guinea was located in the region along the border with Liberia and Sierra Leone.
The WHO had said the worst-affected area, which straddles the borders between the three countries, would be isolated and treated as a “unified zone”.
It is not clear what effect Guinea’s announcement will have on the strategy.
The WHO said a co-ordinated response was essential.
The Ebola virus was first discovered in the Democratic Republic of Congo in 1976.
Experts say the current outbreak is unusual because it started in Guinea, which has never before been affected, and is spreading to urban areas.
[youtube 4FAlu6u9oH0 650]